Identifying Common Causes of Bruises and Bleeding in Children
In the realm of childhood bruises and bleeding, a plethora of causes may lurk, stretching from inconsequential injuries to grave medical conditions lurking beneath the surface. It is not unheard of for youngsters to acquire occasional bruises as they frolic about and experience tumbles or knocks; after all, their delicate skin may be more susceptible than that of their adult counterparts. Yet some children bear the burden of easy bruising or excessive bleeding even when faced with minimal trauma. In such instances, it becomes paramount for parents and caregivers to remain vigilant regarding potential reasons behind this enigmatic bruising and profuse bleeding in order to secure appropriate medical aid.
Hemophilia looms as one possible culprit behind effortless bruising and aberrant bleeding in children – an inherited affliction characterized by blood’s clotting factors being either woefully deficient or utterly dysfunctional. Primarily targeting males, hemophilia can incite unprovoked bleeds without any perceivable injury, prolonged post-injury oozing even after trivial cuts or dental procedures ensue, along with agonizing joint swelling fueled by internal hemorrhages. Leukemia – a cancerous scourge disrupting bone marrow’s production line of blood cells – is another condition intertwined with heightened risk for both bruising easily and spontaneous nosebleeds. By throwing off the delicate balance between red cells (oxygen carriers), white cells (infection fighters), and platelets (clot formation aficionados), leukemia-stricken children might find themselves battling fatigue alongside frequent infections while bearing inexplicable bruises.
While severe disorders like hemophilia or leukemia demand immediate intervention from healthcare professionals; other less alarming yet still noteworthy contributors towards fragile skin include vitamin deficiencies – particularly Vitamin K deficiency playing its critical role in protein activation necessary for efficient clotting processes; together with hereditary connective tissue ailments which render blood vessels weaklings prone to damage culminating into blemish formation upon mere pressure application on affected areas where weakened vessel walls reside. If you observe your child consistently displaying peculiar patterns linked to excessive bleeding episodes following trivial traumas, recurrent spontaneous emergence of multiple small-sized purplish spots indicative of capillary ruptures beneath the skin’s layers, or protracted healing times after injuries despite diligent wound care practices; it is prudent to consult a physician for further evaluation and any necessary investigations in order to exclude underlying inherited bleeding disorders, or other medical conditions meriting swift intervention from healthcare experts.
Recognizing the Symptoms and Signs of Hemophilia in Young Patients
Hemophilia, a bewildering genetic bleeding enigma, predominantly plagues males and can incite bruising and copious bleeding even from trifling injuries. The gravity of this affliction fluctuates among individuals; however, discerning the indicators of effortless bruising or inexplicable hemorrhaging in youngsters may expedite diagnosis and apt management. Hemophilia materializes due to scarcities in clotting factors VIII or IX – quintessential proteins for blood coagulation. Insufficient or malfunctioning clotting factors render it arduous for blood vessels to forge efficacious clots and curb bleeding.
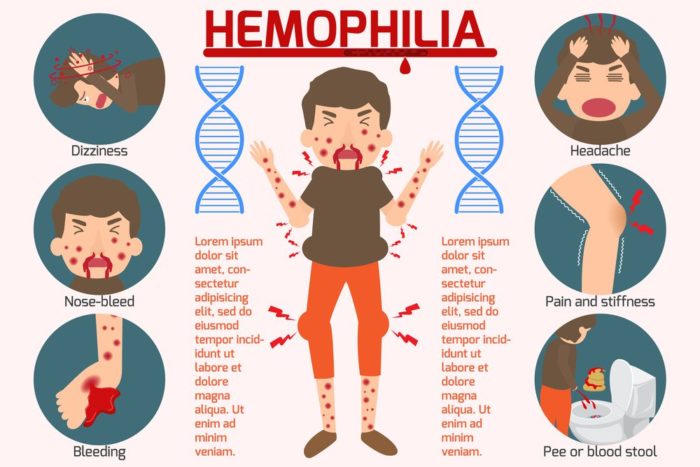
Youth afflicted with hemophilia are prone to facile bruising as their blood vessels lack requisite aid from clotting factors VIII or IX. Effortless contusions may manifest in regions with minimal trauma such as arms, legs, or torso. Besides unprovoked bruises surfacing, other manifestations might encompass protracted nosebleeds, impulsive gum bleeds post teeth-brushing, joint inflammation owing to internal hemorrhaging (hemarthrosis), muscle bleeds eliciting pain and tautness (hematoma), and sanguineous urine (hematuria). It is paramount for parents and caretakers to vigilantly surveil these signs so they can solicit medical care if necessary.
Diagnosing hemophilia entails evaluating a child’s medical chronicles alongside conducting specialized blood examinations that gauge levels of clotting factors VIII or IX. If either factor level is detected considerably below standard range values while platelet count abides within normal boundaries; this could insinuate the presence of hemophilia A (factor VIII deficiency) or B(factor IX deficiency). Blood cell tallies will also be assessed during the diagnostic testing process since any abnormalities related red cells white cells platelets might indicate an underlying issue contributing excessive bleedingsuch leukemia another type disorder unrelated hemophiliacausebruising\n
Leukemia and its Connection to Bruising and Bleeding in Children
Leukemia, that perplexing malignancy of blood-forming tissues, casts a bewildering shadow over the clotting factors and diminutive blood vessels in young patients. The ensuing chaos within these indispensable components frequently manifests as excessive bleeding and bruising. Moreover, children engulfed by leukemia may present diminished levels of clotting factors such as factor IX – an essential player in the formation of blood clots. Thus, afflicted youngsters are prone to increased bruising due to their body’s compromised ability to form clots post-injury.
Furthermore, vitamin deficiency may add fuel to the fire regarding bleeding or bruising issues amidst leukemia-stricken children. In particular, scarcities of vitamins K and C can result in fragile small blood vessels that easily rupture upon minor impacts or pressure fluctuations. Consequently, this heightened vulnerability culminates in youngsters who endure recurrent bruises even from seemingly innocuous activities like engaging in sports or frolicking with peers.
Considering that exorbitant bleeding and bruising can arise from diverse sources – spanning inherited bleeding disorders such as hemophilia or von Willebrand disease to vitamin deficiencies – it becomes crucial for parents and caregivers not only be watchful about monitoring any peculiar occurrences but also promptly seek medical aid if apprehensions emerge. Precocious diagnosis and pertinent treatment interventions are indispensable for effectively managing underlying conditions like leukemia while curbing potential complications tied to debilitated blood clotting capabilities.
The Role of Blood Vessels, Platelets, and Clotting Factors in Bleeding Disorders
The intricate dance of blood vessels, platelets, and clotting factors is vital in enabling the body to fashion blood clots that stave off undue bleeding. The genesis of hemorrhagic maladies in youngsters may stem from anomalies or scarcities within these crucial elements. Hemophilic children, for instance, grapple with specific clotting factor deficiencies that hinder their bodies from effectively forging blood clots. Such predicaments can spawn unbidden bleeding episodes and heightened bruising susceptibility post-minor trauma. Parents and caretakers must be cognizant of their child’s hemophilia diagnosis whilst grasping its impact on quotidian activities.
When blood vessel damage arises or platelet insufficiencies manifest through quantity or function impairments, excessive hemorrhaging can ensue alongside disquieting large-scale bruises devoid of discernible injury origin upon a child’s physique. At times, even mundane endeavors might incite bruising due to feeble vessels or compromised coagulation processes. Frequent inexplicable contusions warrant seeking counsel from a healthcare practitioner specializing in pediatric hematological ailments at your proximate children’s infirmary.
Yet another determinant influencing bruise propensity and bleed likelihood pertains to red blood cell count and efficacy within the circulatory apparatus; deficits therein also have significant bearings on complications endured by those grappling with hereditary hemorrhagic disorders like hemophilia. As an inherited affliction transmitted via familial lineages where certain indispensable clotting factors are either entirely absent or present only meagerly; protracted intervals occur during which external lacerations exhibit sluggish healing while internal bleeding poses grave hazards such as progressive joint deterioration if left inadequately addressed by medical experts versed in this domain\n
Vitamin Deficiencies and Their Impact on Bleeding and Bruising in Children
The perplexing role of vitamin deficiencies in the manifestation of bruising or bleeding among children cannot be underestimated. A dearth in vitamin K, as an illustration, could instigate a disorder that hampers blood’s clotting efficacy. Consequently, this might culminate in extended or excessive bleeding even after trivial trauma or injury. In a similar vein, insufficient levels of vitamin C may render fragile blood vessels and predispose children to bruising from seemingly innocuous bumps.
Healthcare experts employ indispensable blood tests when scrutinizing potential vitamin deficiencies as latent factors for recurrent bruising or bleeding episodes. These assessments aid in ascertaining if imbalances exist within the body’s capacity to generate essential clotting factors and platelets required for standard healing processes. Occasionally, other manifestations such as weariness, pallid skin, joint ache, and hemorrhagic gums could also signify underlying complications with bone marrow functionality – further accentuating the significance of comprehensive medical evaluation.
Parents and caregivers ought to diligently oversee their child’s holistic well-being and pay heed if they discern that their young ones are more prone to bruising than normal or suffer severe bleeding after sporadic bumps or scratches. It is vital not to presume that every infrequent contusion is merely attributable to boisterous play; rather consult with a healthcare professional who can evaluate whether additional probing into possible disorders like hemophilia or leukemia might be justified based on detected patterns of childhood bruises over time. By remaining vigilant about any alterations in your child’s vulnerability towards injury-related complexities such as inexplicable bruises and lingering wounds devoid of improvement signs will guarantee prompt intervention when most necessitated.\n
Seeking Medical Attention for Excessive Bleeding or Bruising in Pediatric Patients
Parents and caregivers, it is of utmost importance to keep a vigilant eye on your little ones, as specific symptoms may hint at a potentially grave health situation lurking beneath the surface. Take for example, excessive bruising or bleeding in our young pediatric patients – an alarming signal indeed! Those with fewer platelets find themselves prone to bruises and might encounter recurring nosebleeds, gum bleeds, or extended blood loss from minor injuries. This proves especially worrisome since platelets are vital players in the blood clotting process; hence, having too few can result in minor wounds that bleed excessively.
A myriad of factors could contribute to increased bruising or bleeding episodes in children. Let us consider hemophilia – more specifically factor VIII deficiency – an inherited ailment characterized by improper clotting due to insufficient levels of blood-clotting factor VIII. Males mainly suffer from this condition because it connects with the X chromosome; females carrying the gene generally do not display symptoms but may transmit it to their progeny nonetheless. Thusly, parents possessing family medical histories featuring hemophilia or related conditions should communicate such information to healthcare professionals so they may explore appropriate diagnostic examinations and treatment alternatives.
To ascertain whether your child’s frequent bruises are merely results of typical childhood playfulness or indicative of something more sinister beneath the surface necessitates examining aspects like location, size, frequency of occurrence along with accompanying manifestations such as fatigue or joint discomfort. Should your child seem unusually prone compared to peers when acquiring bruises easily without significant injury involved then this could potentially signify a grim matter requiring further inquiry by qualified specialists? Instances where inexplicable bruises emerge suddenly alongside deteriorating overall well-being – particularly if accompanied by fever – demand swift medical attention considering potential ramifications linked delay diagnosis intervention strategies targeting root causes responsible these manifestations (e.g., leukemia).
Diagnosing Inherited Bleeding Disorders through Blood Tests and Medical History
The intricate endeavor of discerning hereditary hemorrhage maladies in offspring entails numerous aspects that influence the development of contusions and profuse bleeding. Quite often, guardians observe their progeny’s bruises to be more lingering or recurrent than customary. The emergence of crimson or violet speckles upon the dermis, dubbed petechiae, could signify a concealed coagulation ailment. It is surmised that 9 out of 10 juveniles with acute hemophilia shall undergo unprovoked bleeding ere they attain two years of age.
Examinations involving blood prove crucial in detecting congenital clotting disorders like hemophilia or factor VIII insufficiency. These assessments aid in pinpointing the precise coagulation disorder through gauging levels and efficacy of particular clotting factors present within the circulatory system. For instance, those afflicted with severe hemophilia frequently possess under 1% normal factor VIII action – significantly hindering their capacity to generate clots post-injury. Bleeding can transpire internally into articulations and musculature even after trivial injuries; hence it is vital for medical practitioners to recognize these ailments promptly so fitting therapeutic strategies may ensue.
While assessing a youngster’s medical chronicles concerning potential inherited hemorrhaging disorders, physicians will contemplate occurrences wherein frequent epistaxis arises without seeming reason or protracted bleeding follows minor lacerations or grazes. Spontaneous episodes of hemorrhage manifesting in diverse bodily regions might also heighten suspicions surrounding an underlying condition such as hemophilia. If manifestations are sufficiently grave and accordant with those witnessed amongst individuals suffering from hemophilia or akin conditions, it becomes imperative for parents to consult specialists proficient in pediatric hematological care for additional evaluation and diagnosis via thorough testing measures encompassing analysis pertaining to family history linked with similar matters among kinfolk.
Preventing and Managing Bleeding and Bruising Complications in Children with Hemophilia
Amidst the labyrinthine concerns plaguing parents and caretakers of younglings afflicted with hemophilia, discerning whether a bruise or bleeding event betokens an underlying malady emerges as paramount. Hemophilia induces the cessation of blood clots forming aptly, potentially inciting excessive contusions and hemorrhaging upon the epidermis as well as within sinews, joints, or other visceral structures. The healing process for these manifestations may be protracted compared to those unburdened by hemophilia due to scarceness in clotting constituents coursing through their veins.
When pursuing medical counsel for offspring exhibiting indications of facile bruising or lingering bleeding occurrences, it is vital that healthcare practitioners undertake a comprehensive chronicle and corporeal assessment. This endeavor might encompass inquiries regarding hereditary haemorrhagic disorders within the family lineage, antecedent events pertaining to profuse contusions or bleedings, and any pharmaceuticals presently administered to the patient. In certain instances, clinicians may decree blood examinations corroborating conjectures about an underpinning ailment such as hemophilia based on these revelations.
To forestall complexities affiliated with hemophilic bruises and bleeds, it is imperative that progenitors collaborate intimately with their child’s health management collective at institutes of medicine whilst adhering stringently to directive principles furnished by scholarly research establishments specializing in this realm. By heeding suggested treatment schemes – inclusive of prophylactic coagulation factor transfusions if requisite – conjoined with sustaining transparent discourse amongst all contributors engaged; families can efficaciously regulate potential perils presented by this affliction while concurrently guaranteeing superlative caliber care for their precious ones impacted by this uncommon yet grave disorder.

