Identifying the Signs and Symptoms of Hand, Foot, Mouth Disease
A baffling and sporadic malady, hand-foot-and-mouth disease (HFMD) frequently assails the young ones; however, it is no stranger to grown-ups. The culprits behind this contagious affliction are numerous viruses, with Enterovirus 71 and Coxsackievirus A16 being prime suspects. Early detection of HFMD’s telltale indications is imperative in curbing its dissemination whilst ensuring apt care for those encumbered by it.
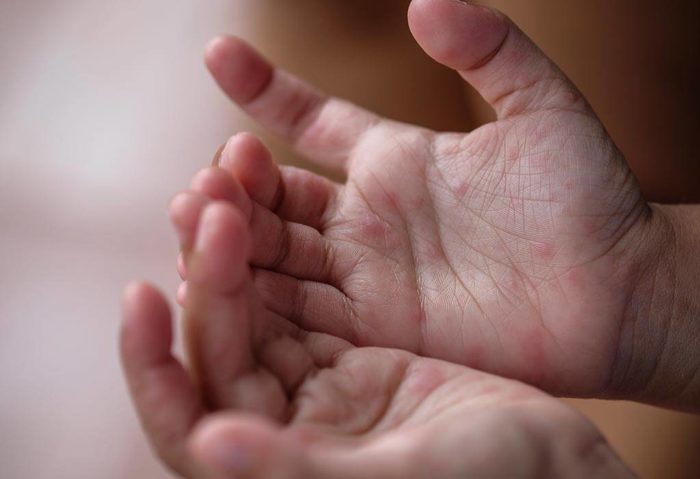

In the early stages of this puzzling ailment known as hand-foot-and-mouth disease, one might discern feverishness, an aching throat, languor, dwindling appetite or general unease. As the infirmity advances unrelentingly forthwith, excruciating oral ulcers may arise concomitant with eruptions adorning extremities – hands and feet alike. Appearing like diminutive crimson specks or vesicles that itch or feel sore when touched; these rashes demand vigilant attention from parents and caregivers suspecting their child to be battling HFMD.
Though some instances of HFMD exhibit mildness sparing complications aplenty; other cases necessitate medical intervention owing to dehydration wrought by challenges imbibing fluids or pain alleviation concerns arising from mouth sores. If your child exhibits such signs betokening hand-foot-and-mouth disease – do not tarry! Swiftly seek counsel from a healthcare practitioner for precise diagnosis and tailored treatment strategies. By actively identifying HFMD at its nascence – you can alleviate your progeny’s discomfort while concurrently impeding contagion amongst your community members.\n
The Contagious Nature of Hand-Foot-and-Mouth Disease
The bewildering malady known as hand-foot-and-mouth disease (HFMD) is an astoundingly contagious ailment, elicited by the enigmatic enterovirus. This affliction predominantly plagues younglings below a decade in age. Manifestations of HFMD encompass feverishness, tender throats, and weariness – succeeded by the emergence of agonizing ulcers within oral cavities and eruptions festooned with vesicles upon extremities, sometimes extending even to posterior regions. Alas! The ease at which these indications can pass from one juvenile to another occurs via direct contact or mere exposure to tainted surfaces.
A veritable cascade of viral transmission unfolds when an individual besieged by HFMD grazes their inflamed blister or rash before coming into contact with the visage or appendages belonging to another soul. Further complicating matters are respiratory droplets laden with virulence cast forth into our shared atmosphere during bouts of coughing or sneezing perpetrated by those afflicted. Moreover, given enteroviruses’ resilience – persisting on surfaces for durations spanning multiple days – it becomes feasible that a person brushing against sullied objects such as playthings in childcare environments might fall prey to foot-and-mouth disease.
A paramount element contributing to the infectious essence of HFMD lies within its incubation epoch – stretching betwixt three and six days post-exposure ere any overt manifestations arise. Within this temporal expanse, unwitting individuals may disseminate viral particles unbeknownst even unto themselves due to their own latent infection status. Compounding this conundrum further is that convalescence from symptoms like rashes or sores adorning hands and feet offers no guarantee against continued contagion; residual traces of enterovirus may linger for upmost 10 days after recovery within saliva or fecal matter bestowing carrier potential upon seemingly hale subjects once more.
Considering all these intricacies intertwined with the habitual propinquity shared by offspring in domestic or daycare environs, swift discernment of hand-foot-and-mouth disease proves paramount for curbing further dissemination amongst susceptible populace.
Virus and Transmission: Understanding the Cause and Spread of HFMD
Encompassed by a cluster of enigmatic enteroviruses, Hand-foot-and-mouth disease (HFMD) finds its most familiar kin in Coxsackievirus A16. Highly infectious, these viral pathogens travel effortlessly through close encounters with tainted individuals or surfaces. The unsuspecting transmission ensues upon contact with the carrier’s saliva, nasal discharge, blister fluid, or fecal matter. It is pertinent to acknowledge that HFMD eruptions commonly besiege childcare environments and educational institutions due to the nearness of children who may lack refined sanitary habits.
The inception of this peculiar ailment presents itself as feverish sensations accompanied by an inflamed throat and perplexing red blemishes adorning the palms, soles, gluteal region, and potentially within the oral cavity. These mysterious spots may evolve into agonizing blisters itching for resolution over time. As these vesicles rupture and mend within a 7-10 day span without scarring; discomfort may plague afflicted souls during this phase. Younglings are particularly vulnerable to dehydration as they might resist imbibing fluids on account of excruciating mouth ulcers. Elder children and grown-ups might bear milder manifestations like coughs or sneezes but still unwittingly disseminate the virus.
To mitigate the potential acquisition of HFMD whilst averting additional flare-ups among kith or classmates in school/childcare milieus; guardians ought to instruct their offspring about upholding exemplary personal cleanliness practices encompassing frequent hand ablutions throughout each diurnal revolution utilizing saponaceous solutions & H2O for no less than 20 seconds preceding thorough rinsing under flowing aqua especially post lavatory utilization or interaction with conceivably contaminated articles/surfaces akin to playthings/tomes/shared implements et al., circumventing commensality/personal item distribution even if overt indicators remain elusive upon external examination (i.e., devoid visible rashes/blisters), concealing one’s olfactory/oral aperture amid expiratory spasms to avert scattering droplets teeming with viral fragments into the proximate atmosphere where others might readily acquire them, and swiftly discarding used tissues/sanitizing sullied surfaces employing fitting germicides. Furthermore, it is vital to consult medical counsel for accurate diagnosis and therapeutic intervention of HFMD symptoms as over-the-counter panaceas like ibuprofen may alleviate pain & fever while shunning aspirin due to its linkage with Reye’s syndrome in juveniles.
The Role of Proper Hygiene in Preventing the Disease
In the realms of preventing hand-foot-and-mouth disease (HFMD) transmission, a highly contagious viral infection that predominantly plagues children, safeguarding proper hygiene is indeed of paramount importance. The ailment manifests itself through symptoms such as mouth sores, rashes gracing hands and feet, along with fever. Comprehending how good hygiene practices can serve as a shield against this common childhood affliction is vital for parents and caregivers.
Enteroviruses are often found guilty of causing hand-foot-and-mouth disease – easily spreading via direct interaction with an infected individual or contact with contaminated surfaces. Saliva, mucus, feces or fluid from blisters may harbor the virus responsible for HFMD; henceforth it swiftly propagates when a child engages in hand-to-mouth contact involving these substances. To thwart the passing on of the virus amongst both young ones and grown-ups alike, endorsing regular handwashing – particularly post toilet visits or diaper changes – proves invaluable as it eradicates germs before they possess an opportunity to infect others. Disinfecting frequently-touched objects like playthings and doorknobs could also diminish the likelihood of disseminating HFMD.
Although signs pointing towards hand-foot-and-mouth disease usually vanish within 7 to 10 days sans medical interference, one must bear in mind that an infected child might remain contagious even if their symptoms have receded into oblivion. In actuality, certain individuals may not exhibit any indications but still be carriers of the virus inducing said malady. Consequently, assiduousness in upholding commendable personal cleanliness continues to hold significance even when no visible illness is present at home or educational environments where young ones are more susceptible due to intimate interactions during leisurely pursuits or partaking food utensils come mealtime occasions. Relentlessly fostering hygienic habits amidst family members and companions will substantially abate potential surges in this pervasive yet avoidable condition affecting both youngsters and adults across the globe.
Recognizing and Treating Common Symptoms: Blisters, Rashes, and Sores
A bewildering and sporadic manifestation of hand-foot-and-mouth disease (HFMD) encompasses blisters, rashes, and sores adorning various bodily regions. Primarily targeting children below five years of age, this viral affliction is not averse to affecting older children and adults. Knowledge of HFMD symptoms becomes paramount for parents and caregivers in ensuring prompt intervention.
Initial indicators often comprise feverish sensations, sore throat or waning appetite, succeeded by agonizing oral sores near the mouth’s anterior portion. Rashes may also be found on hands, feet or buttocks. Effectual management within domestic confines necessitates adherence to rigorous sanitation norms such as frequent soap-and-water hand washing. The twofold benefit includes alleviating discomfort and thwarting contagion spread amidst familial circles or childcare environments.
As no specific treatment exists for virus-induced HFMD – unlike bacterial infections – over-the-counter analgesics like acetaminophen may assuage fever-related anguish under medical supervision. Diligent hygiene practices during outbreaks within households or childcare establishments are imperative; disinfecting commonly touched surfaces might prove vital in curbing transmission.
Parents ought to restrict infected offspring from educational institutions until contagiosity has subsided – usually seven days post-onset but occasionally longer based on individual factors . Despite being a predominantly mild condition that resolves sans complications , swift detection combined with fitting management measures remain essential elements contributing towards minimizing its influence among impacted communities .
The Importance of Proper Diagnosis and Treatment in Children
The cruciality of accurate diagnosis and treatment for hand-foot-and-mouth disease (HFMD) in infants and children cannot be overstated. This prevalent viral affliction, frequently brought on by the Coxsackie virus, primarily targets young ones with manifestations such as mild fever, throat discomfort, and blisters adorning hands, feet, and oral cavities. Discerning these telltale signs at an early stage is of utmost importance to effectively mitigate their severity before they exacerbate or give rise to complications.
Within seven days post-exposure to this pernicious invader do symptoms typically emerge. Noteworthy red flags comprise agonizing ulcers within the oral cavity hindering swallowing; rashes or vesicular eruptions upon palms, soles, knees or buttocks; heightened irritability in infants stemming from unease; diminished appetite; lethargy; cephalalgia; myalgia or arthralgia. Dehydration may ensue in certain instances if afflicted youngsters refuse fluids due to mouth pain. Caregivers ought to remain vigilant that diaper-changing can also serve as a conduit for the virus since fecal matter may harbor it.
To thwart further dissemination of this highly communicable malady amongst kinfolk or other individuals residing together from academic institutions where outbreaks are commonplace occurrences – guardians bear the responsibility of ensuring stringent hygienic practices are adhered to religiously by everyone interacting with an infected child. Frequent ablutions with soap and water – particularly subsequent to utilizing toilet amenities – hold paramount significance in diminishing transmission hazards linked with handling tainted surfaces such as playthings exchanged among children during indoor/outdoor recreational endeavors! Moreover fostering ill juveniles who display any indicative markers thereof maintain distance until full recuperation transpires will aid in curbing likelihoods others contract said ailment too\n
Dealing with HFMD Outbreaks in Child Care Settings
The enigmatic hand-foot-and-mouth ailment, a viral malady frequently tormenting younglings below five years of age, is an oft-encountered scourge in the world of childhood afflictions. Nevertheless, older progeny and grown-ups are not immune to its pernicious reach. The virulent nature of this mysterious disease fosters episodes within childcare environments where contagion flourishes.
Symptoms manifest as feverishness, throat discomfort, oral lesions, and curious eruptions or vesicles adorning hands and feet. Timely discernment coupled with accurate identification of this bewildering condition are paramount for controlling its dissemination.
A puzzling incubation epoch spans three to six days; thus vigilant observation by progenitors and guardians is vital during said temporal bracket. If exposure to the virus seems probable or if offspring bear any telltale signs associated with this illness, sequester them at home until complete recovery precludes further transmission within nurturing establishments. Furthermore, adherence to scrupulous sanitation rituals such as regular ablutions aids in stymieing proliferation of this ubiquitously incited viral onslaught.
Childcare facilitators wield considerable influence in assuaging epidemic flare-ups through stringent sanitary standards enforcement whilst routinely assessing each attending child’s wellbeing status. Acquiring sage wisdom regarding early harbingers that portend potential infection will enable necessary safeguard implementation when outbreaks besiege their facilities. Enlightening personnel on efficacious sterilization techniques employed against HFMD-inducing pathogens shall assist in curbing contamination peril amongst surfaces habitually contacted by affected individuals—whilst concurrently providing suitable care for symptomatic children recuperating within domestic abodes or scholastic surroundings alike\n
Protecting Your Child: Tips for Parents and Caregivers to Prevent HFMD
In the bewildering realm of parenting and caregiving, a paramount responsibility lies in collaborating intimately with one’s progeny’s care squadron to thwart the insidious advance of hand-foot-and-mouth disease (HFMD) – that pervasive malady afflicting multitudes of fledgling humans. An indispensable stratagem for prevention encompasses ensuring your offspring steer clear from those besieged by HFMD, as this pernicious viral interloper remains contagious for a span of 3 to 6 days post symptom manifestation. An exchange of crucial intelligence betwixt parents and caregivers on any incidences of HFMD within their respective domains serves to diminish the perilous transmission amid our younglings.
The pivotal significance of impeccable hygiene reigns supreme in combating HFMD. Guardians must be uncompromising in frequently lathering their hands with soap suds and cascading water – most notably prior to culinary preparation or consumption, following utilisation of lavatories or swapping nappies, and upon encountering bodily secretions such as salivary emanations or nasal expulsions. Inculcating our little ones with exemplary handwashing prowess enables them too to adopt admirable sanitary practices. The diligent sanitation rituals encompassing playthings and surfaces harbouring potential pathogens further curtails the likelihoods for infectious propagation.
Pursuing insights bestowed by accredited healthcare savants apropos diagnosis and remediation is merely one facet; vigilance from parents during their child’s convalescence from HFMD remains an imperative duty. A majority will find solace in spontaneous resolution within a span ranging between seven to ten solar revolutions; nevertheless, should new blemishes materialise on extremities beyond this timeframe or supplementary complications emerge, it becomes vital that consultations ensue promptly with medical professionals for appraisals and guidance anew. Embracing these safeguards assiduously whilst fostering transparent dialogue among all constituents within your cherished child’s care collective shall substantively fortify defenses against this alarmingly contagious viral affliction.

