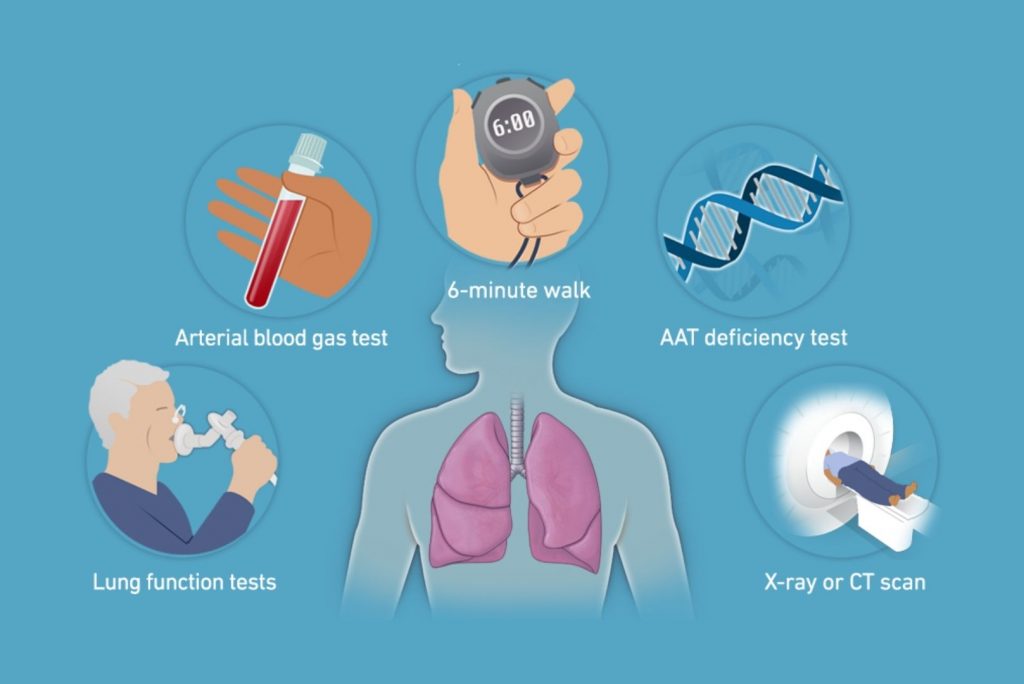
Asthma, a condition that affects millions of adolescents and adults worldwide, is a chronic disease marked by inflammation of the airways. Effective management of asthma hinges on understanding the condition, identifying triggers, and monitoring its progression. At the heart of this is the peak flow meter, a portable device that measures airway flow.
What is a Peak Flow Meter?
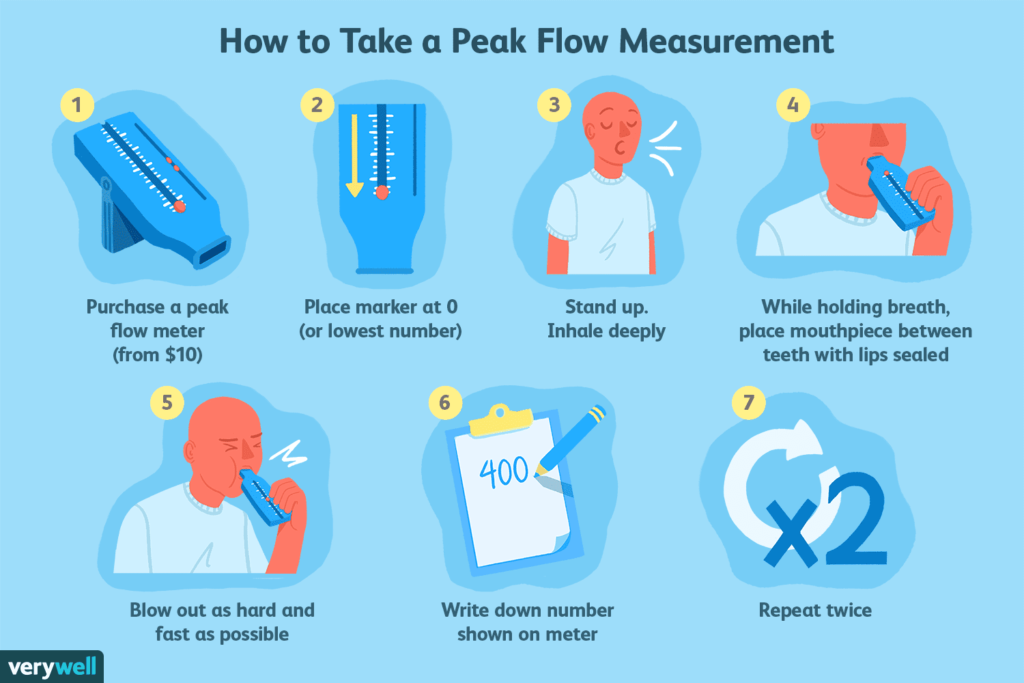
A peak flow meter is a portable device designed to measure the peak expiratory flow rate (PEFR) – essentially, the speed at which air comes out of your lungs when you blow out as hard and as fast as possible. This quick and straightforward procedure can provide invaluable insights into your respiratory health and the state of your asthma.

Why Measure Your Peak Flow?
Regular peak flow measurement serves several essential purposes:
- Monitoring Asthma Symptoms: A drop in your peak flow readings might signal an impending asthma attack or indicate that your asthma is getting worse. Conversely, consistent readings in your normal peak flow zone can reassure you that your asthma is under good control.
- Guiding Treatment Choices: Keeping an asthma diary, where you record your peak flow values alongside any asthma symptoms and medicine usage, can help your healthcare provider tailor your treatment more effectively.
- Recognizing Asthma Triggers: Noticing decreases in peak flow after exposure to potential triggers can help you identify and avoid these factors in the future.
How to Use a Peak Flow Meter
- Preparation: Make sure to use the same peak flow meter every time for consistent results. Before you blow into the meter, ensure the device is at zero.
- Positioning: Stand upright, take a deep breath, and close your lips around the mouthpiece, ensuring no air escapes.
- Exhalation: Blow out as hard and fast as possible into the meter.
- Reading: Note the number you achieved – this is your peak flow reading.
- Repeat: Take your peak flow at least three times, recording the highest peak flow number.
Understanding Your Peak Flow Zones
Imagine a traffic light. Peak flow readings are typically categorized into three main zones:
- Green Zone (80 to 100% of your personal best peak flow number): Asthma is well-controlled. Continue with your asthma action plan.
- Yellow Zone (50 to 80% of personal best): Warning! Your asthma may be worsening. Seek guidance from your asthma action plan and consider adjustments in your asthma medicine or inhaler usage.
- Red Zone (below 50% of personal best): Danger! Your airway might be severely restricted. Seek emergency care.
Benefits of Using a Peak Flow Meter
- Proactive Management: Using a peak flow meter can help in the proactive management of asthma, letting you catch symptoms before they escalate.
- Aid in Treatment: It provides tangible data, aiding healthcare providers in determining the effectiveness of asthma medicine and inhalers.
- Education: It helps you learn more about asthma and your unique triggers, empowering you for better asthma care.
Conclusion
Asthma, though persistent, need not control your life. With tools like the peak flow meter and an understanding of your symptoms, you can have the upper hand. Remember, knowledge is power. So, monitor your peak flow, understand the readings, and always follow your asthma action plan. Together, we can breathe easier.