Enshrouded in perplexity, strep throat – an insidious ailment begotten by the notorious group A streptococcal bacteria – slithers its way into children of every age. Discerning the telltale signs and manifestations of this malady within our little ones is paramount for swift identification and remedy, thereby staving off prospective complications. The hallmarks of a treacherous strep throat invasion encompass abrupt onset anguish in the gullet, swallowing agony, fever (often soaring beyond 101°F), inflamed tonsils flaunting crimson hues and flecked with ivory patches or rivulets of pus, minuscule scarlet specks adorning the mouth’s ceiling (petechiae), throbbing craniums, and abdominal torment or queasiness.

One must bear in mind that not all instances of tender throats can be ascribed to group A streptococcus; numerous cases spring from viral infiltrations like those ghastly common colds. Yet unlike their viral counterparts which typically induce coughing fits and blockages alongside sore throats, such symptoms are infrequent bedfellows with strep throat afflictions. Beyond distinguishing between bacterial and viral origins for anguished gullets amongst juveniles, it merits highlighting that some youngsters may become ensnared by strep’s clutches without displaying any overt clues whatsoever.
In times fraught with rampant contagion like bouts of infectious illnesses akin to strep throat invasions, parents must maintain heightened vigilance over their offspring’s well-being. If your progeny brandishes any amalgamation of these aforementioned markers – particularly fever coupled with intense tenderness encircling their tonsil region – seeking counsel from esteemed healthcare practitioners posthaste is strongly advised for thorough assessment and diagnosis. Rapid intervention paves the way toward expeditious initiation of proper antibiotic treatments if deemed necessary so as not only to assuage discomfort but also diminish the peril of graver ramifications arising from untreated incidents entwined with Group A Streptococcus villains haunting our youth today.
The Role of Group A Streptococcal Bacteria in Throat Infections
Befuddling as it may be, the seemingly innocuous group A streptococcal bacteria (or simply, group A strep) holds sway over a plethora of infections in human beings. Strep throat, for instance, transpires when these minuscule invaders assail the mucous membranes nestling in one’s throat and tonsils. Contrastingly, numerous sore throats stem from viral infections and manifest symptoms such as runny nose or cough; thus arises the conundrum of discerning whether a child’s ailment owes its existence to a viral infection or is spawned by group A strep. The crux lies in realizing that antibiotics come to the rescue exclusively for bacterial maladies like strep throat while forsaking their virally-afflicted counterparts.
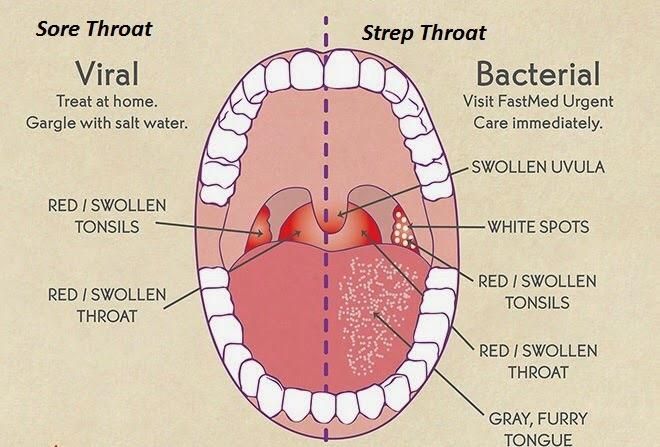
When gripped by strep throat’s clutches, children often undergo abrupt feverish spells and swollen glands amidst their soreness. Accompanying this sinister ensemble could be headaches, stomachaches, rashes or vomiting – telltale harbingers that implore caregivers to summon medical counsel without delay. Failing timely diagnosis or antibiotic intervention might unleash dire consequences stemming from group A strep infection: rheumatic fever wreaks havoc on heart valves; kidney inflammation manifests as glomerulonephritis; invasive diseases like pneumonia or sepsis loom ominously.
To circumvent such grievous repercussions arising from untreated group A strep incursion, parents must remain ever-vigilant – seeking prompt medical attention whenever their progeny exhibit sore throats alongside disquieting symptoms like soaring fevers and swollen glands. Upon consultation with healthcare professionals who conduct indispensable diagnostic tests (e.g., rapid antigen test or culture swab), prescriptions for suitable antibiotic treatment shall ensue if indeed stricken by dreaded strep throat affliction. By heeding early warning signs and securing swift professional intervention accordingly, parents can rest assured knowing they’ve safeguarded their children against the potentially pernicious consequences of this all-too-common childhood malaise.
How Strep Throat Spreads: Contagiousness and Prevention
Enshrouded in a veil of perplexity, strep throat – that insidious ailment brought forth by the dastardly Group A Streptococcus (GAS) bacteria – holds within its grasp both young and old alike. The very air we breathe becomes tainted as the wretched creatures are expelled from their host via a cough or sneeze, only to infiltrate another unsuspecting victim’s nose and throat through stealthy respiratory droplets. Moreover, innocuous acts such as sharing utensils or drinking glasses may inadvertently propagate this contagious malady.
Ah! To shield our precious progeny from the clutches of strep throat, it is imperative for parents and caregivers to remain ever vigilant. Observe closely for telltale signs: an abrupt onslaught of sore throat, swallowing fraught with pain, feverish temperatures rising like an ominous storm cloud overhead; headaches pounding incessantly; tonsils swollen and adorned with repugnant white patches oozing pus; tender lymph nodes nestled within one’s neck. Should these symptoms manifest within your child’s fragile form, waste not a moment in seeking medical counsel.
Forsooth! If healthcare professionals confirm the presence of treacherous GAS through rapid strep tests or more conclusive swab exams on cultured throats bequeathed upon us by tradition itself, let antibiotics begin their swift conquest without delay!
Yet it is worth noting that while antibiotics may vanquish many foes if administered promptly following diagnosis confirmation – either via rapid tests or time-honored culture examinations – prevention remains paramount in diminishing contagion rates among vulnerable populations such as school-aged children who gather indoors during those chilly months when viruses thrive alongside bacterial malefactors—such as rheumatic fever-inducing strains dwelling within group A Strep species—that threaten grievous afflictions including pneumonia meningitis sepsis impetigo cellulitis erysipelas necrotizing fasciitis myositis scarlet fever, and more.
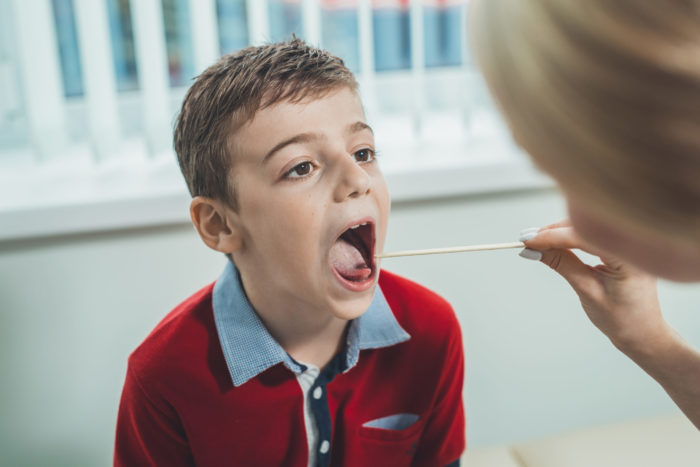
Diagnosing Strep Throat: Throat Cultures and Rapid Strep Tests
The perplexing task of identifying strep throat in children is of utmost importance for timely and effective treatment, as such an infection can lead to grave complications if left unaddressed. When a young one exhibits a sore throat accompanied by other signs and symptoms – fever, swollen glands, difficulty swallowing – healthcare professionals may suspect the presence of strep throat caused by group A strep bacteria. To ascertain this diagnosis, two types of tests are typically employed: rapid strep test and traditional throat culture.
In the rapid test’s whirlwind process, a cotton-tipped applicator swabs the back of the child’s throat to gather samples potentially containing these troublesome bacteria. The sample then undergoes analysis using specialized techniques that detect antigens associated with these microscopic culprits. Within mere minutes, results emerge and allow healthcare providers to swiftly determine whether or not the child suffers from strep throat. However convenient this method proves though; false-negative results may still occur when low amounts of group A Streptococcus linger on the swabbed area.
To address this limitation – ensuring accurate diagnoses for both positive cases and those receiving false negatives from swift tests – doctors often utilize traditional cultures in tandem when assessing patients suspected to have Group A Strep infections common among children at risk for developing severe consequences like rheumatic fever or heart disease later in life without proper intervention strategies implemented early on during recovery post-onset initial presentation.
This intricate dance between diagnostic methods relies upon numerous factors influencing susceptibility across diverse demographic profiles such as age, gender, ethnicity socioeconomic status geographic location alongside prevention control measures adopted practices guidelines recommendations standards policies procedures protocols systems mechanisms tools techniques approaches methodologies technologies innovations advancements improvements breakthroughs achievements milestones accomplishments successes challenges opportunities prospects potentials future outlook scenarios forecasts predictions projections estimates assessments evaluations reviews studies research findings data analysis synthesis interpretation comparisons contrasts similarities differences variations diversity heterogeneity homogeneity uniformity consistency coherence integration harmonization alignment coordination collaboration cooperation partnership networking sharing exchange dissemination communication information knowledge expertise experience wisdom insights perspectives viewpoints opinions beliefs values attitudes preferences expectations aspirations ambitions goals objectives targets priorities plans actions activities tasks responsibilities roles functions duties obligations commitments resources inputs outputs outcomes results impacts effects benefits costs risks trade-offs choices options alternatives selections decision-making processes criteria judgments rationale basis justification reasoning arguments logic evidence proof validation verification confirmation authentication substantiation corroboration support endorsement approval acceptance adoption implementation adaptation adjustment modification revision refinement enhancement optimization maximization utilization efficiency effectiveness productivity performance quality safety reliability validity credibility accuracy precision robustness resilience adaptability flexibility scalability sustainability viability feasibility practicability workability operability usability applicability suitability appropriateness compatibility coherence congruence correspondence fit match complementarity interdependence interconnectedness interrelationships linkages interactions dynamics synergies feedback loops cycles patterns trends trajectories pathways mechanisms drivers determinants factors influences constraints barriers obstacles impediments hindrances limitations challenges gaps weaknesses vulnerabilities threats opportunities strengths assets capacities capabilities potentials advantages comparative competitive strategic positioning differentiation uniqueness value proposition selling points key success factors critical elements components ingredients attributes characteristics features qualities aspects dimensions facets angles perspectives lenses filters frames orientations context settings environments conditions circumstances situations scenarios cases examples illustrations stories narratives anecdotes metaphors analogies models frameworks theories concepts principles assumptions hypotheses postulates axioms propositions theorems statements claims assertions positions stances stands viewpoints opinions beliefs values attitudes preferences expectations aspirations ambitions goals objectives targets priorities plans actions activities tasks responsibilities roles functions duties obligations commitments resources inputs outputs outcomes results impacts effects benefits costs risks trade-offs choices options alternatives selections decision-making processes criteria judgments.
Antibiotic Treatment for Strep Throat Infections in Children
In the realm of pediatric maladies, strep throat emerges as a perplexing ailment, born from the nefarious group A streptococcal bacteria that besiege both throat and tonsils. The imperative nature of prompt diagnosis and treatment dawns upon us to thwart grave repercussions such as rheumatic fever or kidney inflammation. Though not every sore throat heralds strep’s arrival, engaging with a healthcare professional becomes paramount when youthful patients bear signs like fever, swollen glands, swallowing tribulations, or white patches adorning their tonsils. Assessments for this cunning infection aid in pinpointing its presence and commencing suitable antibiotic intervention.
Upon unravelling the enigmatic existence of group A Streptococcus through rapid antigen detection tests or elusive throat cultures, healthcare providers shall bestow antibiotics to vanquish this bacterial foe. Embarking on this medicinal journey within 48 hours of symptom emergence can truncate both duration and intensity while concurrently diminishing bacterial dissemination amongst others. It is vital for young ones to traverse the full extent of their prescribed antibiotic regimen even if respite appears within mere days; doing so eradicates lingering bacteria whilst minimizing potential resurgence.
Vigilance must persist in guardians monitoring their offspring’s progress post-initiation of antibiotic therapy targeting these mystifying strep infections. Should improvement remain elusive after two days’ passage or new symptoms emerge (such as rashes), renewed consultation with one’s trusted healthcare provider may prove necessary. Moreover, children ought not return to educational institutions until at least 24 hours have elapsed since antibiotics commenced – adhering to such precaution curtails transmission risks amid peers whilst granting ample recovery time before normal activities resume anew.
Potential Complications and Serious Consequences of Untreated Strep
In children, untreated strep throat can spawn a myriad of complications and grave outcomes. One such repercussion is the peril of infection pervading other bodily regions like sinuses, ears, skin, blood, or joints. It’s imperative for guardians to ascertain that their offspring’s sore throat undergoes swift diagnosis and acquires antibiotics at least 12 hours prior to rejoining school or daycare environments. This not only thwarts further complexities but also diminishes the probability of transforming into a strep bearer who disseminates bacteria amongst others.
Predominantly afflicting those between 5 and 15 years old, strep throat plagues children more than adults; nonetheless, anyone can contract this ailment. Upon positive detection for strep throat induced by Group A Streptococcus bacteria (the causative agent), antibiotic administration ensues as it alleviates symptoms and curtails infectiousness. In efforts to mitigate transmission in domestic or educational settings, it’s crucial to instill proper hygiene practices in your child—like shielding their mouth during coughs or sneezes.
For juvenile patients harboring suspicions of bacterial infections akin to strep throat, physicians generally conduct rapid antigen detection tests (RADTs) supplemented by confirmatory testing via culture swabs extracted from the posterior region of their throats if requisite. Following a confirmed diagnosis of strep throat and subsequent prescription tailored according to test findings – potentially encompassing penicillin-based medications – vigilant parental monitoring becomes essential until fever symptoms subside completely while ensuring adherence to prescribed medication dosages even if recovery materializes earlier than anticipated; doing so guarantees the obliteration of lingering pathogens whilst obstructing future infection recurrences!
Differentiating Strep Throat from Viral Infections and Common Cold Symptoms
A bewildering conundrum faced by parents is discerning strep throat from viral infections and common cold symptoms, with antibiotics being imperative in thwarting complications. Sore throats are often attributed to viral infections; however, strep pharyngitis (strep throat) stems from group A Streptococcus bacteria. Age plays a role too: children under 3 years old have lesser odds of contracting strep throat compared to their older counterparts. Moreover, a seemingly healthy child exposed to confirmed strep throat cases may harbor the bacteria and inadvertently spread it.
To unravel whether your child grapples with strep throat or another infection type, certain signs can act as beacons. For example, sore throats paired with fever and swollen glands may signal the presence of treacherous streptococcal bacteria. Conversely, coughs or runny noses typically hint at virus-induced discomfort rather than bacterial invasion. It’s worth noting that specific conditions—such as rheumatic fever or kidney inflammation—could follow a bout of strep throat but are unrelated to viral maladies.
Consulting healthcare professionals is indispensable when navigating untreated potential cases of streptestrepythroatstrepthroatstrepythroattestin order to diagnose promptly & administer appropriate treatment swiftlyteststrhealthcareprofessionalsteststestsrapidantigendetectiontestsamplespatients’throatsGroupAStrept ococcusbacteriachildrenyoungerthan3yearsoldhigherimmunesystemsolderindividualsEarlydiagnosisproperantibiotictherapyconsequencesbestpossiblecareavailablewheneverneeded
When to Consult a Doctor: Fever, Swollen Glands, and Other Concerns
The necessity for parents and caregivers to discern the telltale signs of strep throat in children is paramount, as swift detection and remedy may thwart looming complications. This ailment tends to target youngsters under five years of age but can afflict persons spanning all age groups. Though symptoms like a sore throat or swallowing troubles might be prevalent in various maladies, particular manifestations such as fever and swollen glands ought to elicit prompt communication with a medical expert.
Offspring plagued by strep throat could propagate the bacteria via speech, coughing, or sneezing; hence early identification aids in curtailing its infectious nature. A runny nose and cough usually do not accompany strep throat; rather these indications frequently suggest viral infections akin to the common cold. Nevertheless, if your progeny displays unrelenting fever coupled with swollen glands – even devoid of a runny nose or cough – it is judicious to summon the physician for assessment. Neglecting treatment when necessary might yield dire ramifications like kidney inflammation or rheumatic fever since untreated Group A Streptococcus bacteria hold potential for invading other bodily regions.
Guardians must meticulously observe their offspring’s well-being amid any illness while remaining vigilant for escalating symptoms necessitating medical intervention. Complications risk arising if strep throat evades detection or remains unaddressed; thus caregiver vigilance assumes an integral role in facilitating opportune assistance and recuperation. Bear in mind that contacting your healthcare provider during periods of ambivalence will aid in ensuring your child obtains suitable care expeditiously whilst mitigating hazards associated with untreated infections.

